Each department of CSRC assesses various operational risk factors and plans relevant management and control tasks. Internal auditors list high-risk operations as an annual audit plan and they create audit reports from the audit results. They regularly submit reports to the Audit Committee for review and attend the Board of Directors in a nonvoting capacity. In addition, each department conducts selfassessment of the internal control system every year to ensure the effectiveness of system design and implementation. In the future, a dedicated unit shall be established for risk management; more indepth discussions shall be conducted on the Company’s risk management priorities, risk assessment, and response measures; and reports shall be made to the Board of Directors on operational risks and management strategies.
Risk management is an important key to business operations. CSRC enhances decision-making effectiveness and increases corporate value by identifying, managing, measuring, and analyzing the short-, medium-, and long-term impacts of internal and external risk factors. In order to continuously improve the risk management mechanism, we control finance, sales, procurement, and engineering for related internal control issues. Recently, we have focused on the risk management of climate change risks and work safety, and formulated corresponding response strategies and plans. Through the risk early warning system, risk items are regularly tracked and countermeasures are proposed in advance. The system automatically generates warnings about abnormalities, reducing associated labor and avoiding omissions. The validity of the risk identification and early warning process is confirmed through regular audits by the Audit Office. The audit supervisor of the Audit Office regularly explains to the Board of Directors the key points of risk management, evaluates and plans corresponding measures, and reports operations-related risks and management strategies.
Internal Audit Scope
In 2024, CSRC's internal audit unit executed and completed 25 audit reports and six followup reports in accordance with the annual audit plan, proposing a total of 12 internal control recommendations. Areas covered included procurement, acceptance, production management, real estate plant and equipment management, inventory management, sales and receipts, safety and health, and seal management, all tracked and improved in accordance with regulations.
The challenges and responses to various risks of CSRC at this stage are explained as follows:
Risk management and opportunities for climate change
Following the Paris Agreement, climate change response has become an issue that governments and companies must face actively. Domestic and international greenhouse gas emission regulations are becoming stricter, and natural disasters brought about by extreme climates have a direct impact on the operating premises and will all affect the Company’s finances. In response, we have identified risks and opportunities through project meetings based on the TCFD framework (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) and set relevant targets to gradually mitigate climate change. In June 2021, we publicly supported the international TCFD initiative and completed the signing of the TCFD. For detailed information on the management of climate-related risks and opportunities, please refer to section 4.1 Response to Climate Change.
Information Security Risk Management
CSRC complies with personal data protection laws and regulations, ensuring that the collection, processing, and use of personal data are in accordance with legal requirements, and safeguarding the rights and interests of personal data. All relevant data of stakeholders, including customers and employees, are properly recorded and managed. Additionally, the concept of confidentiality of stakeholder information is regularly promoted to all relevant colleagues. For website data collection, CSRC has established a privacy policy, using the collected data solely for businessrelated services. The information is protected by comprehensive information security measures to prevent alteration, deletion, theft, leakage, or unauthorized access. The company has set up a chief information security officer and 3 dedicated information security members on November 9, 2023, a total of 4 people. The information security support team has a total of 30 people, mainly composed of the corporate group- TCC Information Systems Corp. (hereinafter referred to as TCCI) which is responsible for the design of the overall information security architecture, information security maintenance and monitoring, and response and investigation of internal and external information security incidents. The Company's information retention schedule is established based on relevant regulations and requirements, with regular assessments of information security risks to ensure the effectiveness of data protection measures. Additionally, for information security issues, a clear reporting channel is provided to stakeholders (Group Information Security Reporting and Complaint Mechanism Email: service@tcci.com.tw) to promptly identify and address potential risks.
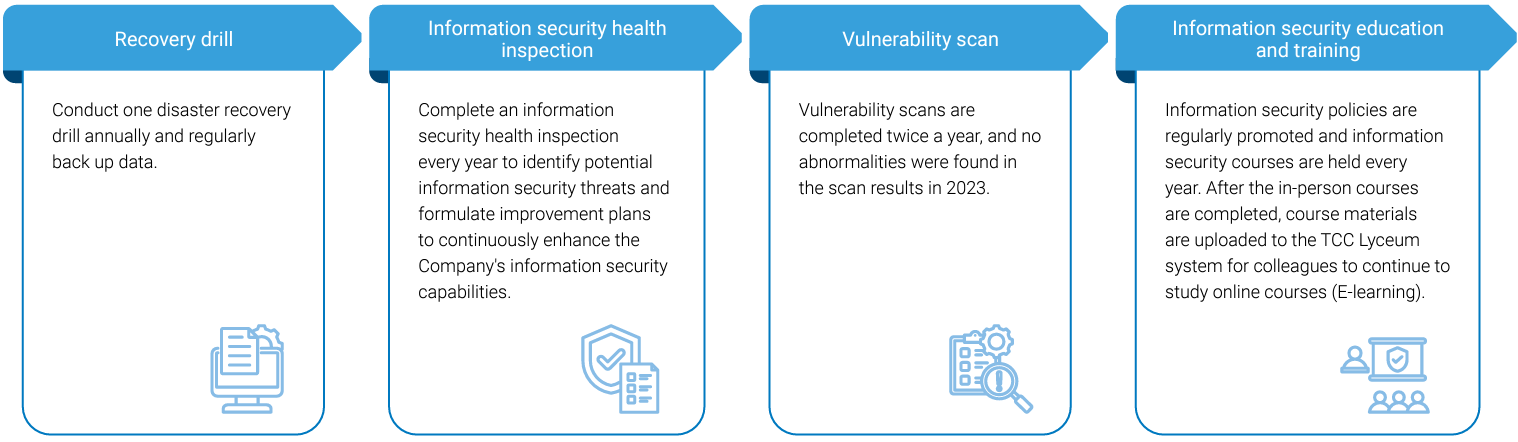
In 2020, the Company established and implemented an information security management system in accordance with the international standard ISO/IEC 27001:2013, adopting the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle operational model. The information security policy is approved by the highest information security unit of the enterprise group, and by the end of 2020, the Company obtained ISO 27001 certification, valid until January 5, 2024. In December 2023, and then successfully completed the transition to ISO/IEC 27001:2022 version certification. Currently, the certificate is valid from January 5, 2024, to January 4, 2027. A cross-departmental Information Security Management Committee is convened by the President, meeting annually to review the effectiveness of information security planning and implementation and significant information security decisions, while coordinating the allocation of necessary resources for information security. An Information Security Management Task Force has been established under the Information Security Management Committee. It is primarily responsible for planning, establishing, implementing, maintaining, reviewing, and continuously improving information security management systems, and reporting information security issues to the Information Security Management Committee. The Information Security Management Task Force holds regular meetings to review the implementation status, and reports the implementation status and review to the Board of Directors on a regular basis every year.
The Company also engages external consulting firms to assist in conducting information security audits to assess the effectiveness of the Company's information security management system. Additionally, external technical firms are commissioned to conduct information security technical tests to inspect the security protection of information systems and websites.
Proportion of factories covered by CSRC’s IT service provider - TCCI certified by ISO/IEC 27001

IRP Information Security Incident Response Plan Flowchart
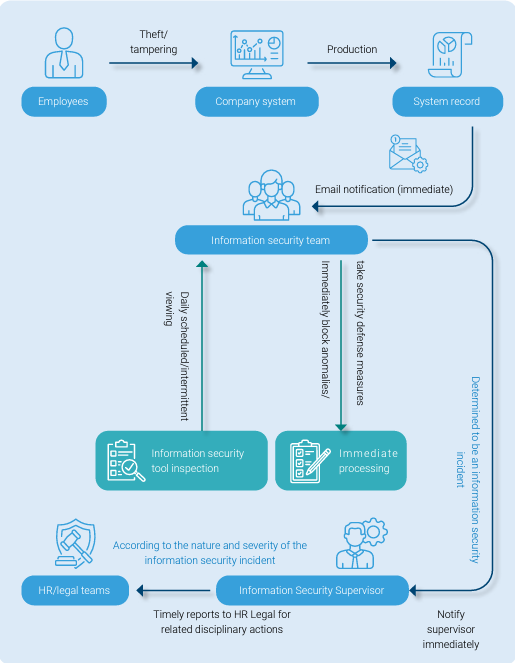
Information security control and protection mechanisms
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Information security organization |
|
| Information security awareness |
2024 processing:
|
| Network security |
|
| Asset management |
|
| Access security |
|
| Physical security |
|
| Data leakage protection |
|
| System security |
|
| Incident detection |
|
| Business continuity |
|
Implementation performance of information security management
In 2024, none of the plants of CSRC received any complaints about customer privacy violations, information leakage, theft, or loss of customer information.
Training Programs on Protecting Personal Data, Preventing Data Leaks, and Maintaining Corporate Information Security

Measures in Response to New Sustainability Information Management Regulations:
Other risk items
Under the existing management measures, there have been no significant abnormalities in the various risks associated with CSRC in 2024.
| Risk | Challenges | Management measure |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management of Unethical Behavior | The scope of dishonest behavior risk management includes: Dishonest behavior such as offering and accepting bribes, providing illegal political contributions, improper charitable donations or sponsorships, unreasonable gifts, entertainment or other improper benefits, infringement of intellectual property rights, and prevention of products or services in a way that is damaging to stakeholders. | In order to prevent occurrences of unethical behavior, a whistleblower system has been established in the form of a "Reporting System of Violations of Professional Ethics." Furthermore, we work regularly through internal control operations, routine audits and so on to reduce the risk of various types of unethical behavior. |
| Financial Risk Management |
The scope of capital risk management includes: Significant capital expenditures are evaluated cautiously and prudently to further enhance the possibility of benefit realization and to set countermeasures for possible derivative risks in advance, so as to reduce and avoid risks that have negative impacts. The financial instruments used by CSRC include equity investments, beneficiary securities investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable, borrowing, and so on, which are prone to exchange rate fluctuations and inflation risks. The exchange rate is mainly affected by fluctuations in the US dollar and RMB market, and since the price of crude oil is linked to the prices of all bulk materials, it will also affect the changes in the cost of raw materials. The extent of the impact on profit and loss depends on the supply and demand of each product market. |
|
| Capital Risk Management | The scope of financial risk management includes equity investments, beneficiary securities investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and loans, which are prone to risks such as exchange rate fluctuations and inflation. | For customers with accounts receivable, the customer's credit status shall be reviewed and the rating shall be provided regularly, as the basis to approve the line of credit, execute sales to the customer on credit, and control accounts receivable, and the anticipated accounts receivable shall be reviewed every month to achieve the objective of zero bad debts for the year. |
| Risk Management of Purchases and Sales |
Purchase risks include: 1. Unexpected risks caused by occurrences in nature, economic policies, price changes and other factors in the procurement of raw materials. 2. The shortage of suppliers with effective sources may increase the risk of supplier chain disconnection. Sales risks include: 1. The continuous increase in accounts receivable can easily lead to excessively high corporate debt-to-asset ratios. 2. Barter is used to offset accounts with one another, and costs have risen and effectiveness has fallen. |
We have established Sales Customer Credit Management Measures and Supplier Evaluation Tasks to regularly evaluate customers and suppliers, evaluate related risk items, and use the SAP system for management and control. |