CSRC strictly controls the use of water resources and continues to improve the efficiency of water circulation to prevent damage to the surrounding environment caused by excessive water intake. Linyuan Advanced in Greater China and the operating plants in the United States have implemented a water balance project and continue to adjust the water resource consumption on a rolling basis. They work with neighboring factories to sell steam to neighboring factories, and the external partners transport the condensate generated in their processes back to the plants for reuse. Other internal water-saving actions include the following: diverting cooling water discharged to the desulfurization absorption tower as a supplementary water source, to expand the scale of water cycle; and regularly examining and repairing leaks in the plant's pipelines to reduce the risk of water waste. In 2024, we continued to take water-saving measures and reviewed the room for improvement in practical operations to achieve the best water resource use efficiency.
Water resource management methods and implementation plan of CSRC

In 2024, CSRC's total water intake was 4,783 thousand m3, which came from third-parties’water, groundwater, well water, and condensate, and the water was used for processes, packaging, and office administration in the Group as a whole. Water intake was 2,321 thousand m3 in Greater China, 1,295 thousand m3 in India, and 1,167 thousand m3 in the United States. The reason for the increase in water withdrawal in the India region in 2024 is the higher production volume at the CCET plant in 2024 compared to 2023.
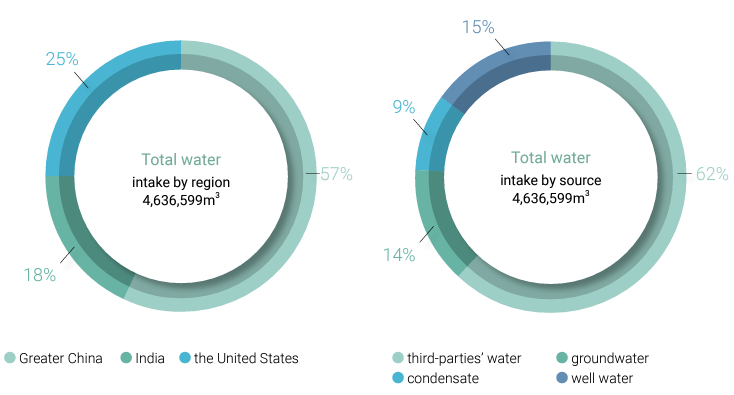
In terms of water resources management, CSRC continues to examine the process water consumption in the plants and implements water conservation and recycling projects to make the most effective use of water resources. In 2024, the wastewater recycling rates of the plants in Greater China were 46% for Linyuan Advanced, 99.9% for Maanshan, 100% for Chongqing and 81.2% for Anshan; the said rates of the plants in India were 100% for CCET and 92.6% for CCIPL; the said rates of the plants in the United States were 100% for CCC Sunray and 100% for CCC Ponca.
● Water risk identification and management
CSRC regularly evaluates overall water risk classification according to the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas by the World Resources Institute (WRI). In Greater China, Taipei Headquarters and Linyuan Advanced are at low-to-medium risk, Maanshan at medium-to-high risk, Anshan at extremely high risk, Chongqing at low-to- medium risk; in India, CCIPL is at extremely high risk. As the main water source of CCIPL is groundwater-tube wells, there is no risk of water shortage. Although CCET is rated as extremely high risk for the overall water risk, the plant is not facing issue of water shortage or flooding. In the United States, the overall water risk of the two plants is rated as low-to- medium risk.
CSRC's operations located in areas of high or extremely high water-stressed account for 32.4% of the group's total water withdrawal. Among these, the wastewater recovery rate reaches 93.6%, and the discharge volume accounts for only 0.22% of the group's total water withdrawal. This demonstrates a strong commitment to valuing and efficiently utilizing water resources, significantly increasing wastewater recovery to alleviate pressure on local water supplies.
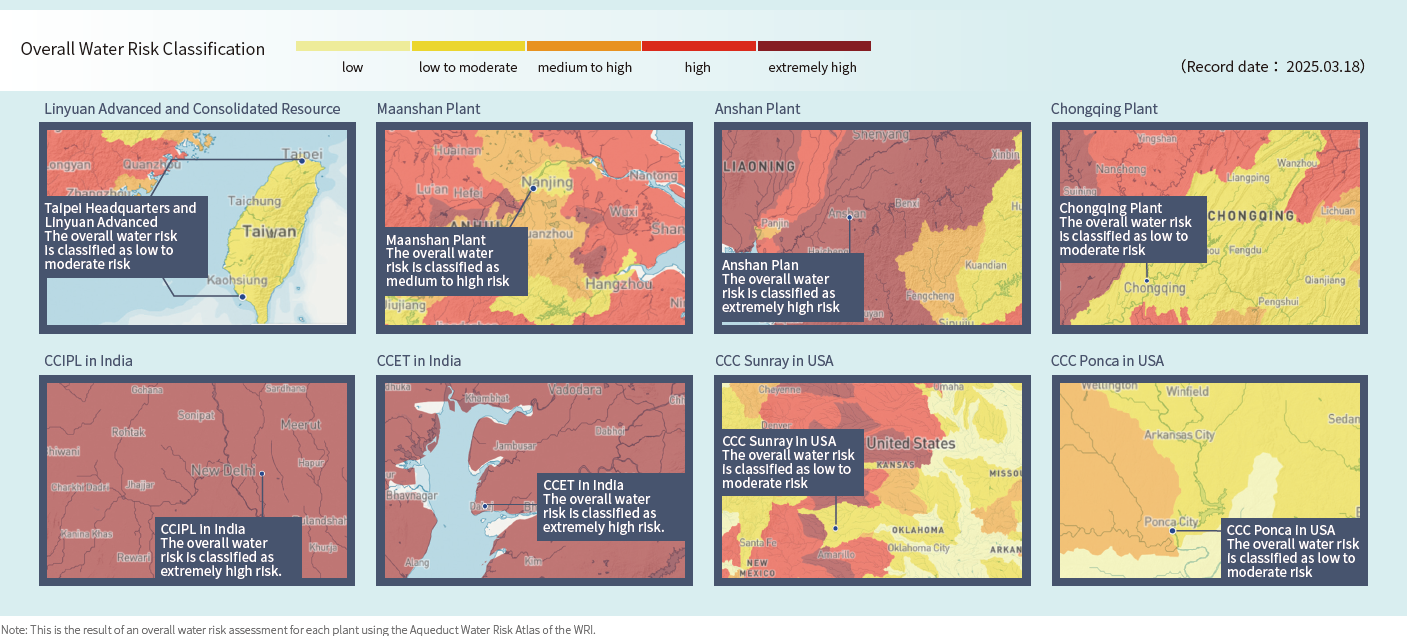
| Note | This is the result of an overall water risk assessment for each plant using the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas of the WRI. |
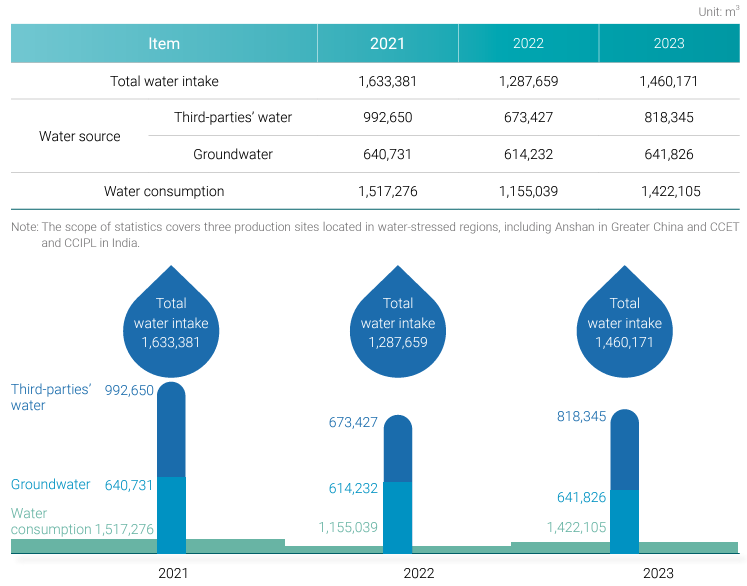
Water intake and consumption by production sites in water-stressed regions
| Item | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total water intake | 1,288 | 1,460 | 1548 | |
| Water source | Third-parties' water | 673 | 818 | 954 |
| Groundwater | 614 | 642 | 594 | |
| Water consumption | 1,155 | 1,422 | 1538 | |
- The scope of statistics covers three production sites located in water-stressed regions, including Anshan in Greater China and CCET and CCIPL in India.
- The reason for the increase in water withdrawal in the India region in 2024 is the higher production volume at the CCET plant in 2024 compared to 2023.
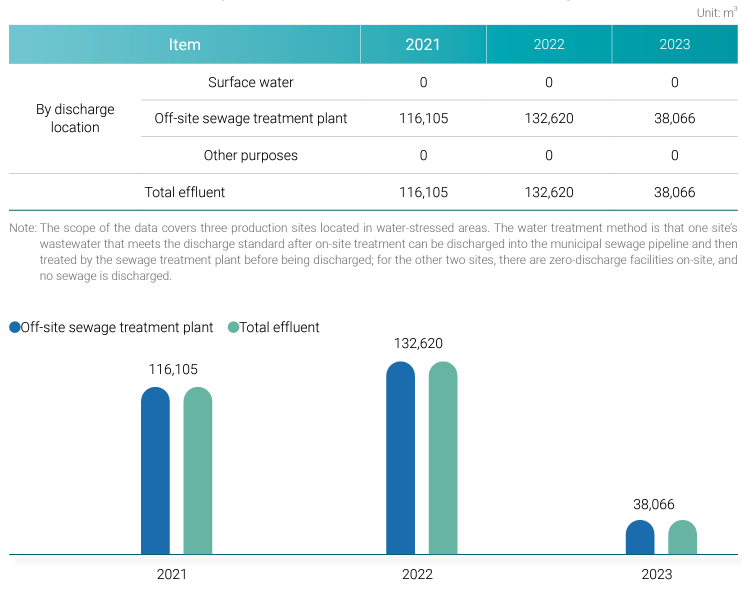
Effluent by production sites in water-stressed regions
| Item | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| By discharge location | Surface water | 0 | 0 | 7.0 |
| Off-site sewage treatment plant | 133 | 38 | 3.5 | |
| Other purposes | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total effluent | 133 | 38 | 10.5 | |
- The statistical scope covers three production sites located in water-stressed regions. Wastewater treatment methods are as follows: Anshan Plant and CCIPL Plant treat wastewater in-house to meet discharge standards before releasing it into municipal sewage systems for further processing by sewage treatment facilities. CCET Plant is equipped with zero-discharge facilities, resulting in no wastewater discharge.
- Due to production and sales adjustments in 2024, Anshan Plant operated fewer hours compared to 2023, leading to a reduction in wastewater discharge compared to the previous year.
In 2024, the Greater China region recorded a water intake of 2,321 thousand cubic meters (m³). Water usage significantly declined compared to 2023, as all plants in the region implemented improvements in process waste heat recovery and steam condensate reuse. The water sources in the Greater China region all come from tap water, not natural water bodies, reducing the environmental impact of water withdrawal. To safeguard against potential droughts or water shortages, the Anshan Plant maintains an emergency water reserve of 3,000 m³ to ensure operational continuity. Plants across the region actively pursue water-saving initiatives and improve wastewater recovery rates. Notably, the Maanshan Plant received the local government’s Water-Saving Enterprise Award for the third consecutive year in 2024.
CCIPL's water intake in India comes from tube wells of groundwater; CCET's water intake comes from tap water. In 2024, the water intake of the plants in India was 1,295 thousand m³. In the United States, CCC Sunray's water sources are rainwater, tap water, and water circulated in the process and the steam production process. Rainwater is collected through the drainage system and ponds in the plant, and the water is treated and used in the process. CCC Ponca's water sources are tap water and well water. Both plants have set up their own zero-discharge facilities for sewage, without sewage discharge to avoid impact on the local water environment. In 2024, the water intake of CCC two plants was 1,167 thousand m³

- After receiving the award in the first year, the title of Water-Saving Enterprise must be maintained through annual evaluations by the local government. Since receiving the award in 2022, the Maanshan Plant has passed every annual evaluation, and thus the 2022 certificate and list are presented.
Group-wide data of water resources over the past three years
| Item | Greater China | India | USA | Group | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | ||
| Total water intake | 2,877.9 | 2,624.7 | 2,321.0 | 614.2 | 849.5 | 1,295.1 | 1,190.8 | 1,162.4 | 1,166.5 | 4,682.9 | 4,636.6 | 4,782.6 | |
| Water source | Third-parties' water | 2,877.9 | 2,617.2 | 2,311.1 | 0 | 207.7 | 701.4 | 41.1 | 64.2 | 55.7 | 2,919.0 | 2,889.1 | 3,068.2 |
| Groundwater | 0 | 0 | 0 | 614.2 | 641.8 | 593.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 614.2 | 641.8 | 593.7 | |
| Condensate | 0 | 7.5 | 9.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 499.3 | 422.3 | 419.7 | 499.3 | 429.8 | 429.6 | |
| Well water | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 650.4 | 675.9 | 691.1 | 650.4 | 675.9 | 691.1 | |
| Wastewater discharge | 250.7 | 167.2 | 113.4 | 0 | 0 | 7.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 250.7 | 167.2 | 120.4 | |
| Water consumption | 2,627.2 | 2,457.5 | 2,207.6 | 614.2 | 849.5 | 1,288.1 | 1,190.8 | 1,162.4 | 1,166.5 | 4,432.2 | 4,469.4 | 4,662.2 | |
| Wastewater discharge rate | 8.7% | 6.4% | 4.9% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 5.4% | 3.6% | 2.5% | |
- Water intake is for process, packaging, and office administration.
- Water consumption = water intake - wastewater discharge
- Wastewater discharge rate = wastewater discharge ÷ water intake
- In addition to third-parties’ water and condensate, Linyuan Advanced uses rainwater but has not yet installed a flow meter, so the data is not available.
- The Greater China region includes the data of Taipei headquarter and Consolidated Resource.
- The increase in water usage in the India region is due to the CCET plant starting production on its first line at the end of 2022, with full-line production throughout 2024, leading to higher output and increased water usage compared to 2023.
- The CCIPL plant, due to maintenance of its wastewater treatment equipment in 2024, generated a discharge of 19 KL/day (below the government-permitted limit of 500 KL/day)
Water consumption and Wastewater discharge for each region in the past three years
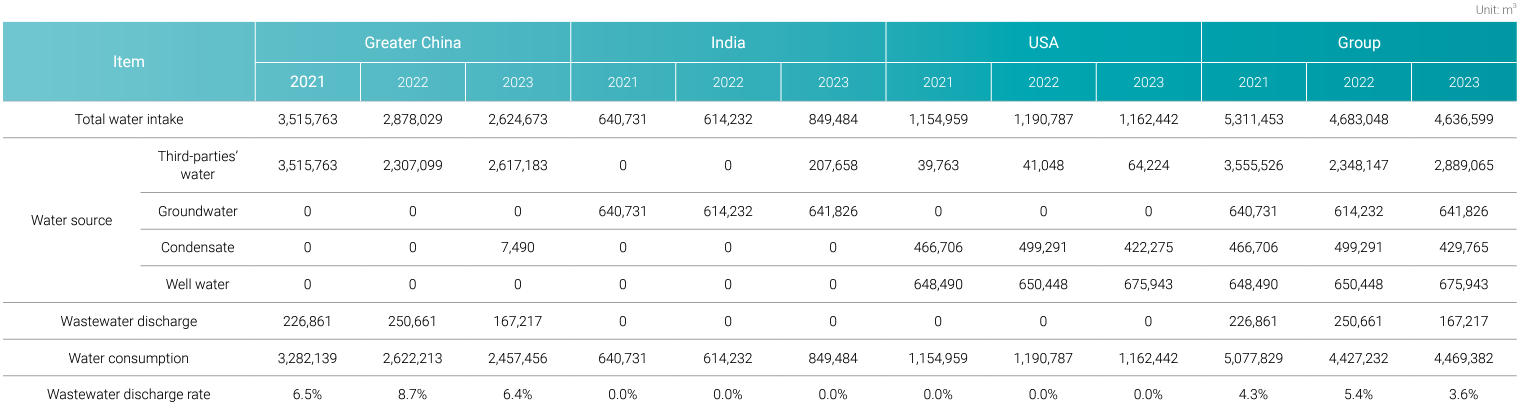
Group water resource management implementation plan

● Water balance project
Linyuan Advanced in Greater China has implemented a water balance project since 2020. By adding flow meters to the process equipment, it aims to effectively keep abreast of the water consumption in the plant and has set the ultimate goal of achieving zero wastewater discharge. Reducing water-related risks in the face of the threat of climate change. We also supply steam to our nearby partners, who then return the condensate generated from their manufacturing processes to Linyuan Advanced in Greater China for reuse, in order to achieve the economic benefits of water recycling. In 2024, a total of 9.9 thousand m3 of condensate was used (accounting for 0.4% of the total water intake of Linyuan Advanced in Greater China). It is estimated that our partners can provide nearly 1.2 tons of condensate per hour (maximum volume is 20 tons). CCET has set up a condensate recycling system, which is still in the testing stage.


CCC has a quench water system, with POTW running 24/7 at a flow rate of 400 gpm, except for Fridays). During normal operations, the risers are filled with water from the pond through the pond pump. POTW pump fill the tank to ensure a continuous supply of quench water. POTW pumps can also be used to fill risers directly.
Rainwater and drainage from green plants are collected in rainwater reservoirs and pumped into the rainwater tank.
There are four emergency pumps in total. Units 1 and 2 are equipped with one active emergency pump and one standby emergency pump.
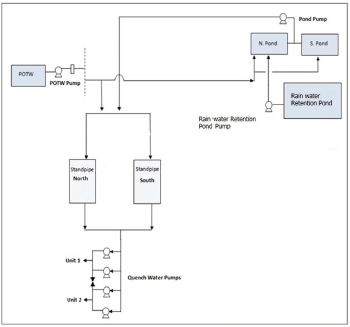
Each plant has set up sewage treatment facilities in accordance with local regulations and standards to treat the pollutants in the process wastewater to meet the management standards of the industrial zone or purifies wastewater and reuses it as process water, in an effort to use resources in a circular economy model. Maanshan and Anshan have also formulated internal wastewater treatment regulations to regulate the operation of wastewater treatment equipment, abnormal accident handling procedures, and occupational safety requirements to ensure the efficient management of the sewage treatment plants and achieve the purpose of water purification. Plants in both the United States and India have effluent treatment plants (ETP) on-site, which not only save water but also avoid the discharge of wastewater, and have formulated a zerodischarge policy. In 2024, CSRC 's regional operations were not in violation of water quality-related laws and regulations.
Effluent treatment method and final discharge location
| Production site | Effluent treatment method and final discharge location | |
|---|---|---|
| Greater China | Linyuan Advanced | The generated wastewater is treated physically and chemically within the plant and then discharged into the Linyuan Industrial Park Wastewater Treatment Plant in Kaohsiung, ultimately being released into the sea. |
| Maanshan Plant | Maanshan has signed an effluent discharge agreement with the Cihu High-tech Zone Wastewater Plant, to agree that wastewater must be treated on-site first until it fully meets the discharge standards before being discharged to the Cihu High-tech Zone Wastewater Plant and eventually to the Yangtze River in China. | |
| Anshan Plant | Wastewater is managed by the local government. Once the discharge standards are fully met, wastewater is discharged to the Dongtai Wastewater Treatment Plant for treatment and eventually discharged into the Nansha River in China. | |
| Chongqing Plant | All the wastewater in the plant is treated and reused, and no sewage is discharged. | |
| India | CCIPL | Wastewater is managed by the local government. Once the discharge standards are fully met, wastewater is discharged to the government notice place. |
| CCET | The plant is equipped with zero-discharge facilities, and no sewage is discharged to avoid impact on the local water environment. | |
| USA | CCC Sunray | The plant is equipped with zero-discharge facilities, and no sewage is discharged to avoid impact on the local water environment. |
| CCC Ponca | The plant is equipped with zero-discharge facilities, and no sewage is discharged to avoid impact on the local water environment. | |
Internal disposal and reuse:
- Carbon black manufacturing: Treated reclaimed water is returned to the carbon black manufacturing process to ensure water resource efficiency and minimize our operational footprint.
- Steam production: The treated reclaimed water is also used to generate steam, which is critical to all stages of our operations.
Wastewater recycling rate of CSRC’s plants over the past three years
| Region | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greater China | Linyuan Advanced | 100% | 56% | 46% |
| Maanshan Plant | 80% | 90% | 99.9% | |
| Anshan Plant | - | 22% | 81.2% | |
| Chongqing Plant | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| India | CCIPL | - | 100% | 100% |
| CCET | 41% | 100% | 92.6% | |
| USA | CCC Sunray | 97% | 100% | 100% |
| CCC Ponca | 100% | 100% | 100% | |
| GROUP | 82% | 89% | 80.3% | |
- Wastewater recycling rate = reclaimed water volume / (reclaimed water volume + water discharge)
Due to the characteristics of the industry, the wastewater discharged by CSRC contains carbon black particles and a small amount of grease. Each regional plant has built-in sewage treatment systems or has commissioned nearby treatment plants, and discharges wastewater in accordance with the sewage discharge standards set by the local governments. In 2024, the quality of effluents from each plant met the effluent discharge standards.
desulfurization tower wastewater, and purified water system wastewater. After treatment of coagulation, pressurized flotation, and sand filtration, wastewater is returned to the production process for reuse. However, the wastewater from the desulfurization tower and the purified water process cannot be recycled at present, so the pH value in the plant is adjusted to neutrality, and SS and COD are strictly controlled to ensure that the water quality is in compliance with regulations before it is discharged to the Linyuan Industrial Park’s sewage treatment plant for subsequent processing. Maanshan has formulated the Wastewater Treatment Plant Operating Procedures for internal management with reference to "IATF 16949-2016 Quality Management System for the Automotive Industry," "ISO 9001-2015 Quality Management System," and "GB/T 19022-2003 Measurement Management System - Requirements for Measurement Process and Measuring Equipment," to regulate the sewage treatment process and ensure that the discharge quality meets the standards. Anshan has also formulated "Wastewater Treatment Plant Operating Procedures" as per "Liaoning Provincial Comprehensive Wastewater Discharge Standards", to standardize the plant's sewage treatment process, abnormal accident handling procedures, and occupational safety requirements, to ensure that the sewage treatment plant can be effectively managed and can operate as expected. The sewage treatment procedures of both plants include grit chambers, air flotation equipment, and silica sand filters. In addition to being used for washing of floors in the plants, part of the qualified treated sewage is returned to the clean water tank for use in the production process, and the remaining sewage is discharged to the sewage treatment plant. All the wastewater inside Chongqing is recycled and reused, without wastewater discharged outside.
CCET in India have zero-discharge sewage treatment facilities in place (as shown in the figure below). The treated water is not discharged outside the plants but recycled in zero liquid discharge (ZLD) plant and returned to the production process and will not discharge any liquid wastewater into surface water. The plants in the United States do not have sewage discharge equipment, and sewage is not discharged to other sewage treatment plants. All water is discharged to the evaporation pond for treatment and then recycled and reused.

Effluent quality from plants in Greater China over the past three years
| Greater China | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linyuan Advanced Plant | Maanshan Plant | Anshan Plant | Chongqing Plant | |||||||||||||
| Water quality parameters | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Minimum standards | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Minimum standards | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Minimum standards | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | Minimum standards |
| pH | 8 | 7.9 | 7.7 | 6~9 | 6.9 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 6~9 | 7.4 | 7.52 | 7.6 | 9 | 7.6 | 8.3 | - | 9 |
| COD(mg/L) | 14.3 | 16.9 | 17.8 | 90 | 14 | 24 | 30 | 300 | 37 | 23 | 95 | 300 | 56 | 109 | - | 500 |
| SS(mg/L) | 3.2 | 5.1 | 17.2 | 25 | 32 | 18 | 8.5 | 400 | 16 | 21 | 5 | 300 | 7 | 30 | - | 400 |
| Grease(mg/L) | 1.6 | 3.7 | 4.8 | 10 | 0.39 | 2.61 | 0.77 | 10 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 20 | - | - | - | - |
| Phenols(mg/L) | 0.0054 | ND | ND | 1 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.020 | 0.5 | ND | ND | ND | 0.5 | - | - | - | - |
| Ammonia nitrogen(mg/L) | 0.59 | 19.5 | 8.6 | - | 0.079 | 0.12 | 0.34 | 25 | 3.69 | 1.57 | 1.0 | 30 | 2.15 | 13 | - | 45 |
- If the sample analysis result is below the method detection limit, it is indicated as ND (Not detected).
- Linyuan Advanced Plant complies with the "Linyuan Industrial Zone User Wastewater Discharge into Sewer System Water Quality Standards."
- The India and U.S. regions do not directly discharge wastewater to any wastewater treatment plant, so no relevant testing data is available.