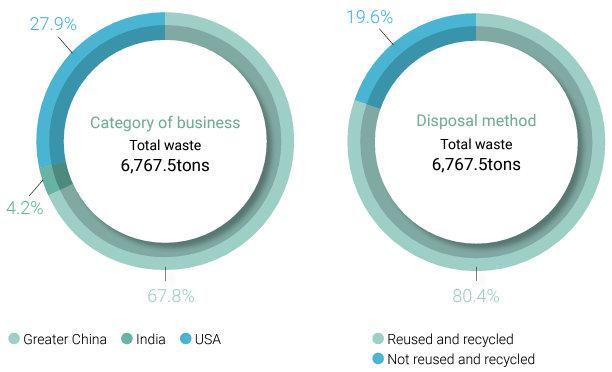
CSRC complies with various waste disposal laws and regulations to ensure that all waste generated is properly disposed of. In order to live up to the spirit of responsible production and circular economy, each plant has kept abreast of the source, type, and quantity of various waste resources, and ensured that their disposal methods and flows are in compliance with all environmental laws and regulations, to further achieve the goals of cleaner production, resource recycling and industrial waste reduction to achieve the goals of pollution reduction, waste reduction, and environmental protection. In 2024, the Group achieved a waste recycling rate of 78.9%, of which 84.5% in Greater China, 89.5% in India, and 73.1% in the United States. Each plant within the group will continue to strive for waste reduction improvements to achieve short-term goals.
In 2024, CSRC Group's total waste generation was 13,308 metric tonsNote, a decrease from 13,727 metric tons in 2023, primarily due to enhanced waste management at the Ponca plant in the U.S., which reduced non-hazardous waste output.
Note: Total waste generated = non-hazardous waste + hazardous waste
CSRC's material input & waste output flow chart
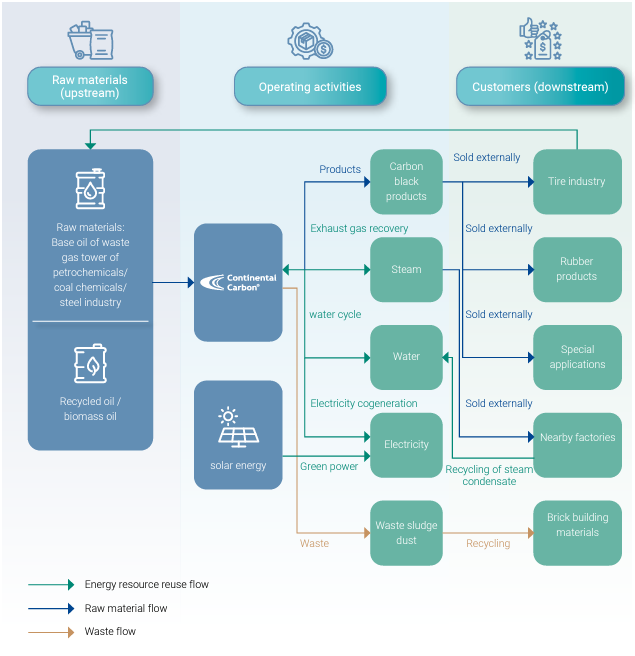
CSRC's waste management process

All CSRC plants in Greater China manage waste in accordance with local regulations. The Linyuan Advanced Plant achieves a waste recycling rate of 79.3%. To reduce waste emissions and enhance reuse, the plant implements thorough waste sorting, effectively collecting and planning for recyclable materials while minimizing general waste transportation costs and incineration volumes. Additionally, the plant has established a dedicated reuse zone, where pallets recovered from clients are categorized into three types for reuse: (1) pallets in good condition are sold to vendors in need, (2) remaining pallets are reused within the factory, and (3) damaged, unusable pallets are processed through the waste disposal system.
Waste generated at the Maanshan, Anshan, and Chongqing plants is managed in compliance with mainland China regulations, with all waste handled off-site. Waste is sorted into industrial waste, recyclable waste, and hazardous waste, temporarily stored in designated hazardous waste areas, and transported by licensed third-party organizations to authorized hazardous waste disposal facilities for legal treatment. Specifically, the Maanshan Plant achieved a waste recycling rate of 99.6% in 2024, primarily through the recycling of desulfurization gypsum and sewage sludge, which are repurposed into cement and brick -based construction materials like bricks, with the remaining general industrial waste recycled for power generation through incineration. The Anshan Plant recorded a 90.9% waste recycling rate in 2024, mainly through incineration and various recycling initiatives, including desulfurization gypsum repurposed for cement production, as well as the recycling and reprocessing of scrap iron, steel, PP bags, and pallets. At the Chongqing Plant, hazardous waste is disposed of through incineration as required by regulations, while non-hazardous waste is landfilled. All waste is temporarily stored in hazardous waste areas and transported by licensed third-party organizations to authorized hazardous waste disposal facilities for legal treatment.

CCET in India has formulated relevant standard operating procedures for waste collection, removal, and disposal. Waste insulation materials, waste petroleum sorbent pads, chemical sludge, and evaporators should be placed in the specified containers, and hazardous waste should be stored in specified hazardous sites and disposed of at the TSDF facilities and incineration plants registered according to the GPCB. In order to manage waste, CCET has obtained membership from a third party authorized by the government. The total waste generated by CCET in India in 2024 was 1063 metric tons, 857 tons of which was non-hazardous waste gypsum. The waste recycling rate in 2024 was 98.7%. CCIPL is equipped with a confined space for the storage of hazardous waste, and its disposal is outsourced to qualified hazardous waste treatment companies. The waste removal and disposal are strictly controlled to reduce the impact on the environment. The plant implements a waste classification and packaging system and packages waste according to types and regulatory requirements to prevent leakage from causing environmental pollution. To avoid hazards to humans, personnel are required to use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow regulations during waste handling, loading, and transport to disposal facilities. CCIPL constantly reviews and updates its waste management policy, hoping to effectively reduce waste and increase waste recycling. In 2024, CCIPL total amount of waste was 355 tons.
All waste generated by CCC Sunray in the United States is in compliance with laws and regulations, and qualified third parties are appointed for disposal. All waste is landfilled, and the plant does not generate hazardous waste. The same types of materials are recycled and reused in the plant to actively reduce waste output. CCC Sunray waste generated in 2024 was 120.9 tons. The waste generated by CCC Ponca in the United States is landfilled, and recycled in accordance with the laws and regulations of the United States. CCC Ponca total waste in 2024 was 7,054.5 tons, and the waste recycling rate was 74.3%, mainly for hydrated lime for roadbed stabilization and agricultural use.
Waste amount of CSRC over the past three years
| Greater China | India | USA | Group | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Type | Disposal Location | Disposal Method | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| Non-hazardous waste | Off-site | Incineration (energy recovery) |
577.6 | 506.5 | 336.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 577.6 | 506.5 | 336.8 |
| Incineration (excluding energy recovery) |
44.4 | 0.0 | 18.7 | 0.0 | 21.1 | 101.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 44.4 | 21.1 | 120.2 | ||
| Burial | 510.7 | 108.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 10.2 | 905.9 | 914.1 | 921.8 | 1416.6 | 1022.8 | 932.0 | ||
| Heat treatment | 144.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 144.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| Physical handling | 310.0 | 237.3 | 513.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 310.0 | 237.3 | 513.6 | ||
| Recycling | 3181.9 | 2785.3 | 2475.3 | 123.0 | 206.8 | 1270.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3304.9 | 2992.1 | 3745.9 | ||
| Others | 145.5 | 226.3 | 637.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 546.8 | 706.6 | 890.2 | 692.3 | 932.9 | 1528.1 | ||
| On-site | Burial | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 15.7 | 3.4 | 120.9 | 15.7 | 3.4 | 120.9 | |
| Recycling | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6849.3 | 7224.5 | 5242.5 | 6849.3 | 7224.5 | 5242.5 | ||
| Total | 4914.5 | 3864.1 | 3982.4 | 123.0 | 227.9 | 1382.3 | 8317.7 | 8848.6 | 7175.4 | 13355.2 | 12940.6 | 12540.0 | ||
| Hazardous waste | Off-site | Incineration (energy recovery) |
178.1 | 506.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 178.1 | 506.1 | 0.0 |
| Incineration (excluding energy recovery) |
1012.2 | 216.2 | 709.2 | 41.7 | 27.6 | 13.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1053.9 | 243.8 | 723.0 | ||
| Burial | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 0.0 | 31.6 | 23.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 31.6 | 25.5 | ||
| Recycling | 0.0 | 4.2 | 17.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.2 | 17.2 | ||
| On-site | Recycling | 3.4 | 0.6 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.4 | 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| Subtotal | 1193.7 | 727.1 | 729.9 | 41.7 | 59.2 | 37.6 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1235.9 | 786.3 | 767.5 | ||
| Total | 6108.2 | 4591.2 | 4712.3 | 164.7 | 287.1 | 1419.9 | 8318.2 | 8848.6 | 7175.4 | 14591.1 | 13726.9 | 13307.5 | ||
| Waste recycling rate | 74.3% | 92.9% | 84.5% | 74.7% | 72.0% | 89.5% | 82.3% | 81.6% | 73.1% | 78.9% | 85.2% | 78.9% | ||
- In the Greater China region, Linyuan Advanced uses stabilization treatment as the alternative disposal method for non-hazardous waste; Anshan plant uses recycling and selling as the alternative disposal method for non-hazardous waste.
- The first production line of the CCET plant in India was commissioned at the end of 2022, therefore there is no data for 2022.
- In USA, due to different definitions of waste in 2022-2023, the production volume of desulfurization gypsum was not included in the calculations. Therefore, the data for 2022-2023 has been retrospectively corrected.
- Waste recycling rate = [volume of recycled waste (including heat treatment, physical treatment, recycling, and sales of the recycled) + volume of waste incinerated with energy recovery] ÷ total waste generated.