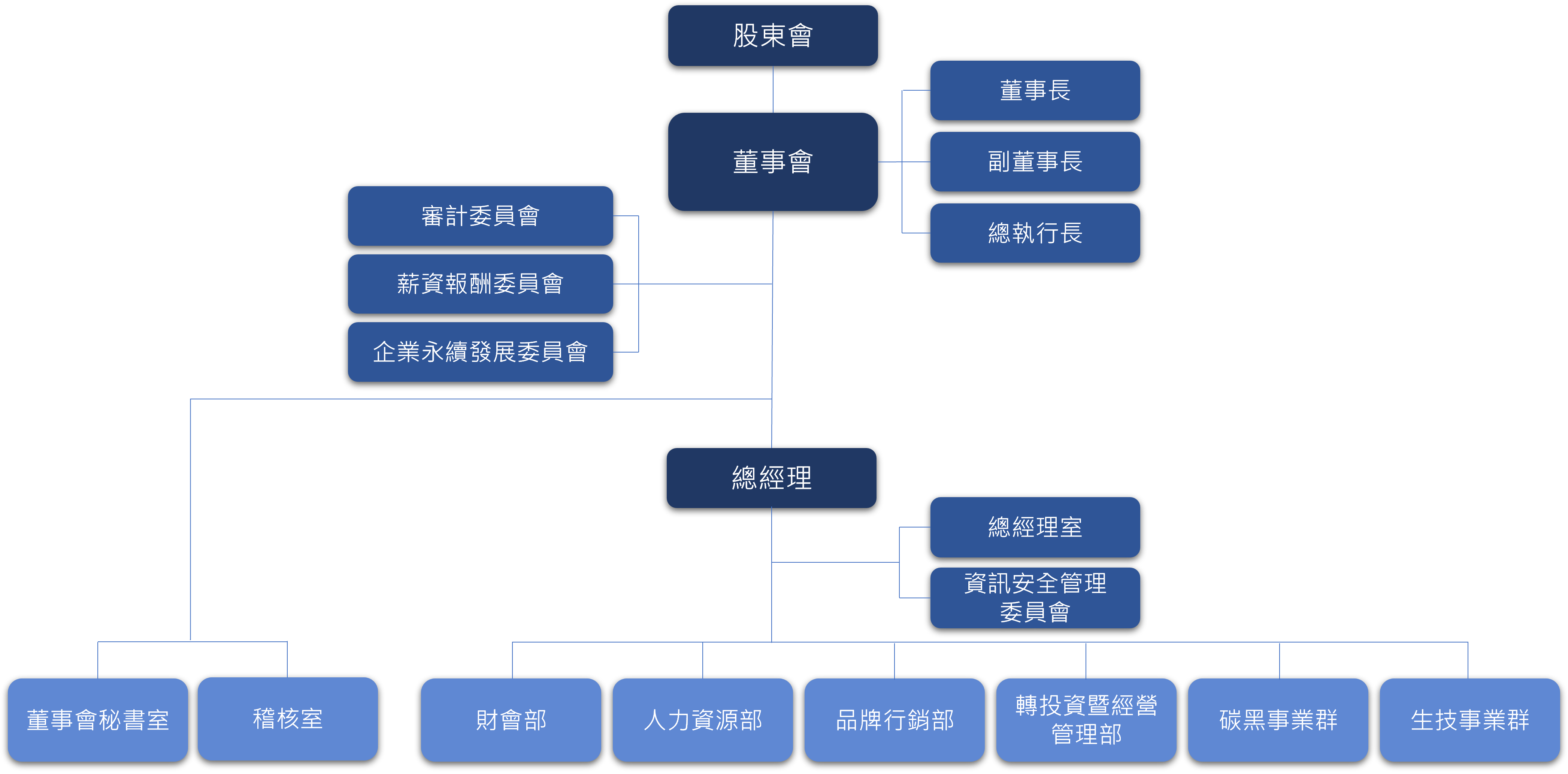
永續發展
企業永續發展委員會
為確保企業社會責任之落實,國際中橡依「企業社會責任政策」設置企業永續發展委員會,負責審查企業社會責任報告書、審定 ESG 各面向年度目標、追蹤及檢討 ESG 各面向實施成效等,確保公司企業社會責任的落實。
委員會每年至少應召開一次,且國際中橡為了強化企業社會責任與公司經營理念的連結,由董事長擔任主任委員,總經理擔任副主任委員,董事、獨立董事 3~4 人擔任委員,各權責單位由該單位最高主管擔任小組成員。除委員及各小組組長例行與會外,每次會議召開得由主任委員依議案內容邀集小組成員參加。各小組應由小組組長選派幹事乙名,負責該小組職掌事項之聯繫溝通與協調,彙整該小組職掌相關資料之提供等事務。
委員會下設誠信治理小組、循環製造小組、永續環境與產品小組、員工照顧小組、社會關懷小組,且另制定「企業社會責任實務守則」、「公司治理實務守則」、「誠信經營守則」等規範,確保公司日常營運融入企業社會責任理念。
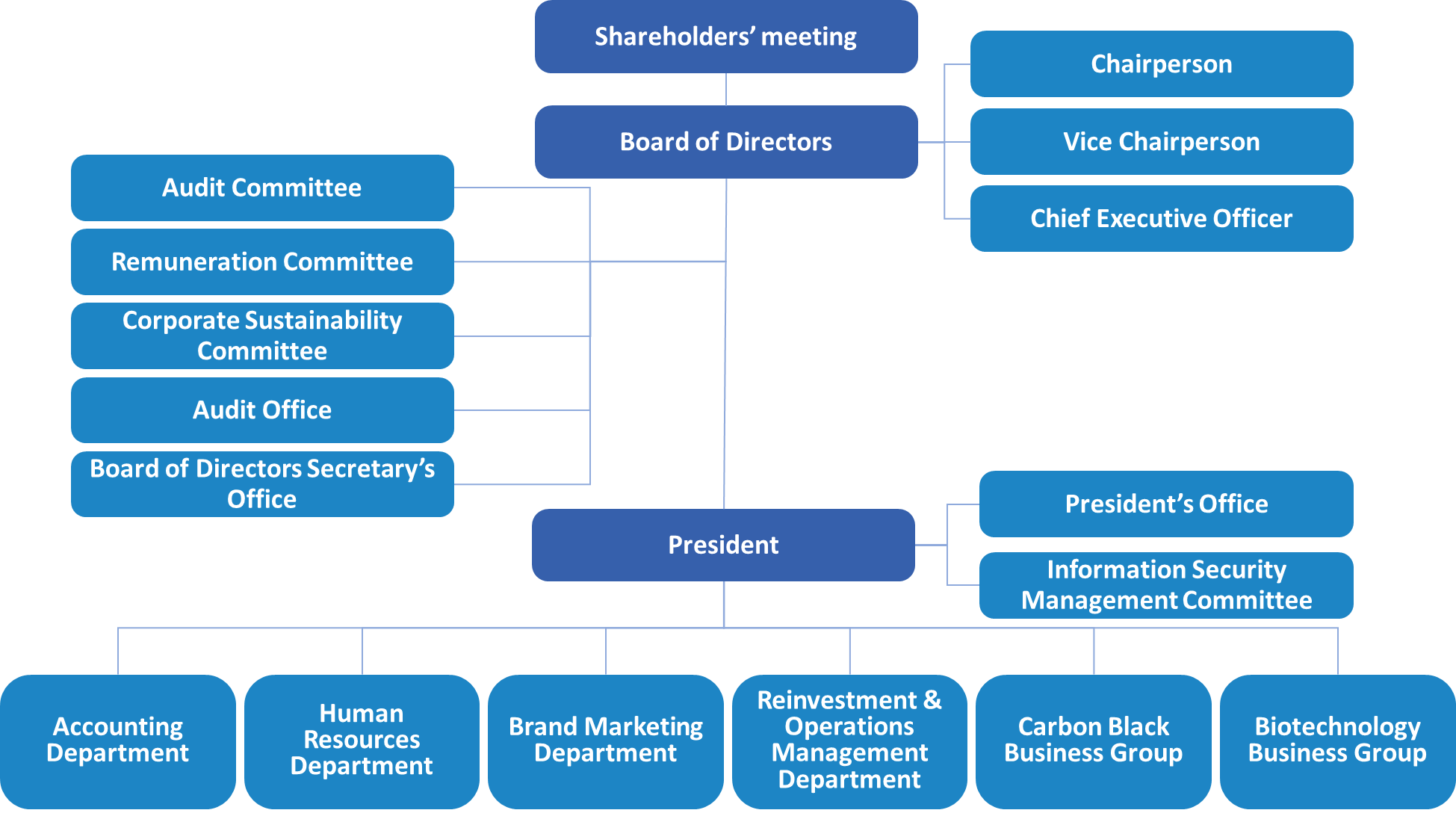
In addition to striving for the greatest achievements in our core business, CSRC Group also actively maintains good interactions with all stakeholders and fulfills its corporate citizenship responsibilities through concrete actions to build a sustainable society.

Corporate Sustainability Committee
To ensure actions taken to realize corporate sustainable development, CSRC established the Corporate Sustainability Committee in 2018 in accordance with the "Corporate Social Responsibility Policy" and upgraded the committee to a functional committee as approved by the Board of Directors (hereinafter referred to as the "Committee"), with the Chairman and two independent directors serving as members. To improve the overall implementation of the Company's sustainable management, the Committee is responsible for reviewing the sustainability reports and identifying stakeholders’ sustainability issues of concern, while being in charge of formulating the Company's sustainability policies, key performance indicators, goals, and plans for each functional group, and reviewing implementation performance. In addition to the routine operations, the Committee regularly reports to the Board of Directors on the targets and the implementation of the policies formulated. The Committee convenes one meeting at least every six months, which may be flexibly adjusted as necessary, but it should convene at least one meeting per year.
To strengthen the connection between corporate sustainability and business operations, CSRC has established an Ethical Governance Team, a Circular Manufacturing Team, a Sustainable Environment and Products Team, an Employee Care Team, and a Social Care Team under the Committee. The top executive of each responsible unit serves as the Committee members. In addition to the routine meetings between team members and team leaders, the chair may invite team members to participate in each meeting according to the content of the agenda. Each team leader should designate a secretary for their team, who should be responsible for contacting, communicating, and coordinating the duties of the team, while compiling information based on the duties of the team. CSRC has also formulated the "Corporate Social Responsibility Best Practice Principles," "Corporate Governance Best Practice Principles," and "Ethical Corporate Management Best Practice Principles" to ensure that the concept of corporate social responsibility is integrated into the Company's daily operations.
風險管理
國際中橡以誠信為基礎,營運理念為基於廉潔、透明及負責之準則,落實公司治理之運作,以及健全風險管理之機制,以創造永續發展之經營環境。國際中橡依法訂定各種內部規章,針對各項風險因子,進行評估後規畫各項管控工作,同時據以執行,且內部稽核人員會將高風險作業列為年度稽核計畫,並將稽核結果作成稽核報告,定期提交審計委員會審閱及列席董事會報告;此外,各部門每年度進行內部控制制度自行評估,以確保制度設計及執行之有效性。
氣候變遷的風險管理與機會
最主要的氣候風險:《巴黎氣候協定》於 2016 年生效的背景下,世界各國開始訂定氣候稅等因應措施。由於國際中橡是一家全球運營公司,因此該地區國家法規的變更將對公司的能源價格和生產成本產生直接或間接的影響。
管理辦法:積極減少 CO2 排放、將設備升級為高效設備、投入脫硝與脫硫污染防制設備、監控系統上線,隨時監控廢水與空汙排放狀況、廠區內增設太陽光電系統、有效回收製程尾氣,轉化成蒸汽再利用及發電。我們的許多工廠已獲得或旨在獲得 ISO 14064 的認證。
最主要的氣候機會:國際中橡碳黑事業群為循環經濟典範,我們將石化 / 煤化 / 鋼鐵業之製程殘餘物 (塔底油),轉化為碳黑銷售,蒸氣亦可銷售或自行發電,提高能資源 (水、電) 使用效率,降低區域內污染,有效降低環境衝擊和改善環境品質。另外,在氣候變化日趨明顯下,生態環境、自然資源受到的衝擊將會更大,地球資源更顯珍貴,因此為調適氣候變遷風險,綠色產品將是國際中橡進一步提高市場份額的機會。
機會策略:我們採取的行動是透過製程優化,持續提升原料油轉化為碳黑之效率,以及透過回收製程尾氣,將熱能轉化成蒸汽,銷售於鄰廠或將蒸汽轉換為動能,發電自用,充分利用循環經濟,為能資源產業盡一份心力。另外,針對綠色產品,國際中橡亦研發 LH 及 SATIN BLACK 系列碳黑產品,可延長輪胎及橡膠製品壽命,減少能資源耗用,珍惜地球資源。
不誠信行為風險管理
國際中橡為落實防範不誠信行為發生,訂定有「違反從業道德行為檢舉制度」之吹哨者制度,並定期透過內部控制運作、例行性稽核等方式,以降低各類型不誠信行為之風險。公司並建立有效的會計制度及內部控制制度,針對不誠信行為風險較高之營業活動,嚴查是否有外帳或保留秘密帳戶。內部稽核人員不定期檢討制度之設計及執行是否持續有效,且定期查核前項制度遵循情形,作成稽核報告提報董事會。
進貨或銷貨風險管理
國際中橡進貨以碳黑原料乙烯焦油、蒽油及煤焦油為主,台灣廠區除與既有國內主要油品供應商維持穩定的合作供應關係,另以進口油品降低供貨短缺與價格波動之風險。中國大陸廠區除維持與各地區當地鋼廠之良好合作關係外,也同時積極開發與焦化廠之合作,避免貨源過度集中,以獲得最佳進油價格。
在銷售方面,因主要客戶均為輪胎業大廠,財務體質健全,過去收款情況正常且良好。此外,公司業務部門對客戶均有額度控管,且定期針對客戶進行徵信程序,避免銷貨集中及應收帳款呆帳之風險。
資本風險管理
資本管理著重於完善的營運計畫,國際中橡依據營運計畫以維持充足資本,支應各項業務之擴展及建設之所需。因此維持良好的獲利能力及財務結構,才得以支應未來中長期所需之營運資金、資本支出、債務償還及股利支出等需求。
財務風險管理
國際中橡使用之金融工具包括權益投資、受益證券投資、應收帳款、應付帳款及借款等,容易產生匯率波動與通貨膨脹等風險,匯率主要受美元、人民幣市場波動的影響,另外則因原油價格連動各項大宗物資價格,亦會影響原物料成本之變動,對損益影響程度則視各產品市場供需情況而定。財務管理部門統籌協調國內外金融市場操作。透過風險程度與廣度分析之內部風險報告,監督及管理相關之財務風險。另設有經營管理分析部門,密切注意各項重要原物料價格變化及供需狀況,定期檢討採購計畫購買情形。
針對應收帳款客戶,定期審核客戶信用狀況給予評等,據以核定信用額度,執行放款客戶銷售、應收帳款之控管,且每月對預期之應收帳款提出檢討,達到年度零倒帳管理目標。國際中橡亦投保相關保險以規避營運風險,如火險、營運中斷險、地震險、颱風及洪水險、第三人責任險、董事及經理人責任險等,降低災損造成的損失針對應收帳款客戶,定期審核客戶信用狀況給予評等,據以核定信用額度,執行放款客戶銷售、應收帳款之控管,且每月對預期之應收帳款提出檢討,達到年度零倒帳管理目標。國際中橡亦投保相關保險以規避營運風險,如火險、營運中斷險、地震險、颱風及洪水險、第三人責任險、董事及經理人責任險等,降低災損造成的損失。
資訊安全風險管理
為因應企業永續經營所面臨的風險及其所帶來的機會與挑戰,除了將資訊安全深耕並落實在日常業務的執行外,遵循國際資安政策標準(如: ISO 27001、NIST),持續完善治理面及技術面之安全基礎架構、強化資安防禦設備、安全情資分析與教育訓練等,從管理到技術,全面提升資安防護能力,降低因資安事件造成業務中斷的風險,以確保企業資訊服務的使用及資料都有最好的保障,達到 2019 年全年度無任何資安漏洞事件發生。
此外,為提升資訊安全治理,規劃成立「國際中橡資訊安全管理委員會」,資安管理委員會負責審視各子公司資安治理政策,監督全集團資安管理運作情形,並定期向董事會報告資安治理概況。另外委由臺泥資訊股份有限公司,負責全集團資訊安全治理、規劃、督導及推動執行,以建構全方位的資安防禦能力及同仁良好的資訊安全意識。
智慧財產管理計畫
本公司在碳黑、電池及生技三大事業主軸,持續投入技術研發領域,結合公司營運目標,發展智慧財產管理策略,並積極鼓勵員工創新及自主研究,提升產品品質及品牌形象,落實產業循環再生經濟之理念及精神。
-
專利管理
鼓勵創新,制定專利獎勵辦法,激勵員工提出發明申請,並建立專利申請審查制度,以內部個案專利申請審議程序,控管專利申請品質。藉由宣導及教育訓練,建立及培養員工保護智慧財產權觀念。
-
商標管理
以全球品牌布局之規劃,積極於世界各國申請商標註冊,並定期檢討商標維護必要性,有效管理商標。
-
著作權管理
不定期向人員宣導、建立正確的版權意識,並於員工任職時要求遵守著作權法,避免使用侵害他人權利之相關著作。
-
營業秘密管理
對於涉及技術開發、技術合作之工程或採購案件,要求商業夥伴均應配合簽署保密協議。員工聘僱契約中訂有要求員工任職期間或離職後,均應負保密義務,不得洩漏公司營業秘密。訂定資訊安全政策與相關資訊管理辦法,強化資訊安全。
執行情形
- 本公司將定期提報智慧財產相關事項至董事會,最近一次提報日期為 111 年 12 月 15 日。
-
關於智慧財產權管理相關事項,本公司近年來的主要執行情形如下:
時間 工作項目 2019 年 5 月及 9 月 - 舉辦二場研發人員之美國專利訴訟及專利管理之教育訓練。
- 定期與事務所盤點商標與專利權之申請與維護情況。
- 要求供應商所提供之產品或服務,應有不侵害他人智慧財產權之擔保聲明。
2020 - 制定專利獎勵辦法,鼓勵同仁積極創新,落實研究發展成果。
2021 - 本公司將透過教育訓練持續提昇員工的智慧財產保護觀念,並持續結合公司營運發展目標為商標、專利權之申請註冊與使用。
2022 - Organize advanced courses on patented inventions for R&D personnel.
-
取得智財清單與成果
-
專利:
截至 111 年 10 月 31 日止,本公司全球專利申請件數共 63 件,其中已通過之「發明」專利 50 件,共計 50 件;審核中之「發明」專利 13 件。
-
商標:
截至 111 年 10 月 31 日止,本公司全球商標申請件數共 144 件,已註冊公告者 126 件,申請中 18 件。
-
專利:
Risk Management Policy
Each department of CSRC assesses various operational risk factors and plans relevant management and control tasks. Internal auditors list high-risk operations as an annual audit plan and they create audit reports from the audit results. They regularly submit reports to the Audit Committee for review and attend the Board of Directors in a nonvoting capacity. In addition, each department conducts self-assessment of the internal control system every year to ensure the effectiveness of system design and implementation. In the future, a dedicated unit shall be established for risk management; more in-depth discussions shall be conducted on the Company’s risk management priorities, risk assessment, and response measures; and reports shall be made to the Board of Directors on operational risks and management strategies.
Risk management and opportunities for climate change
Following the Paris Agreement, climate change response has become an issue that governments and companies must face actively. Domestic and international greenhouse gas emission regulations are becoming stricter, and natural disasters brought about by extreme climates have a direct impact on the operating premises and will all affect the Company’s finances. In response, we have identified risks and opportunities through project meetings based on the TCFD framework (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures) and set relevant targets to gradually mitigate climate change. In June 2021, we publicly supported the international TCFD initiative and completed the signing of the TCFD. For detailed information on the management of climate-related risks and opportunities, please refer to section 4.1 Response to Climate Change.
Information Security Risk Management
The Company's dedicated information security unit is primarily entrusted to TCC Information Systems Corp. (hereinafter referred to TCCI) under the Taiwan Cement Group for overall information security architecture design, information security operations and monitoring, internal and external information security incident response and investigation. The company has set up a chief information security officer and 3 dedicated information security members on November 9, 2023, a total of 4 people. The information security support team has a total of 28 people, mainly composed of the corporate groupTaiwan Cement Information Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as TCC Information) Responsible for the design of the overall information security architecture, information security maintenance and monitoring, and response and investigation of internal and external information security incidents.
The Company's compliance with the ISO/IEC 27001 information security system in 2020: In 2013, CSRC adopted the PDCA cycle operating model as the international standard, establishing and implementing an Information Security Management System. The information security policy is approved by the highest information security unit of the enterprise group, and by the end of 2020, CSRC obtained ISO 27001 certification, valid until January 5, 2024. In December 2023, CSRC successfully completed the transition to ISO/IEC 27001:2022 version certification. Currently, the certificate is valid from January 5, 2024, to January 4, 2027. A cross-departmental Information Security Management Committee is convened by the President, meeting annually to review the effectiveness of information security planning and implementation and significant information security decisions, while coordinating the allocation of necessary resources for information security. An Information Security Management Task Force has been established Under the Information Security Management Committee. It is primarily responsible for planning, establishing, implementing, maintaining, reviewing, and continuously improving information security management systems for information systems, and reporting information security issues to the Information Security Management Committee. The Information Security Management Task Force holds regular meetings to review the implementation status, and reports the implementation status and review to the Board of Directors on a regular basis every year.
The Company also engages external consulting firms to assist in conducting information security audits to assess the effectiveness of the Company's information security management system. Additionally, external technical firms are commissioned to conduct information security technical tests to inspect the security protection of information systems and websites.
Other risk items
| Risk | Challenges | Management method |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management of Unethical Behavior | The scope of dishonest behavior risk management includes: Dishonest behavior such as offering and accepting bribes, providing illegal political contributions, improper charitable donations or sponsorships, unreasonable gifts, entertainment or other improper benefits, infringement of intellectual property rights, and prevention of products or services in a way that is damaging to stakeholders. | In order to prevent occurrences of unethical behavior, a whistleblower system has been established in the form of a "Reporting System of Violations of Professional Ethics." Furthermore, we work regularly through internal control operations, routine audits and so on to reduce the risk of various types of unethical behavior. |
| Financial Risk Management |
The scope of capital risk management includes: Significant capital expenditures are evaluated cautiously and prudently to further enhance the possibility of benefit realization and to set countermeasures for possible derivative risks in advance, so as to reduce and avoid risks that have negative impacts.
The financial instruments used by CSRC include equity investments, beneficiary securities investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable, borrowing, and so on, which are prone to exchange rate fluctuations and inflation risks. The exchange rate is mainly affected by fluctuations in the US dollar and RMB market, and since the price of crude oil is linked to the prices of all bulk materials, it will also affect the changes in the cost of raw materials. The extent of the impact on profit and loss depends on the supply and demand of each product market.
|
|
| Capital Risk Management | The scope of financial risk management includes equity investments, beneficiary securities investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and loans, which are prone to risks such as exchange rate fluctuations and inflation. | For customers with accounts receivable, the customer's credit status shall be reviewed and the rating shall be provided regularly, as the basis to approve the line of credit, execute sales to the customer on credit, and control accounts receivable, and the anticipated accounts receivable shall be reviewed every month to achieve the objective of zero bad debts for the year. |
| Risk Management of Purchases and Sales |
Purchase risks include:
Sales risks include:
|
We have established Sales Customer Credit Management Measures and Supplier Evaluation Tasks to regularly evaluate customers and suppliers, evaluate related risk items, and use the SAP system for management and control. |